Hybrid Proteins: The Future of Sustainable and Nutritious Meat Alternatives
Hybrid Proteins: The Future of Sustainable and Nutritious Meat Alternatives
The global demand for meat is skyrocketing. Driven by rising incomes and a growing population, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) project a 14% increase in meat consumption over the next decade compared to the 2018-2020 average. While this surge reflects changing dietary preferences, it also highlights a pressing problem: traditional meat production is unsustainable, unhealthy, and ethically fraught.
Enter hybrid proteins—a groundbreaking innovation that blends plant-based ingredients with lab-grown (cultivated) meat. These products aim to deliver the taste, texture, and nutrition of traditional meat while addressing the environmental, ethical, and health concerns associated with conventional livestock farming. In this article, we’ll explore the rise of hybrid proteins, their benefits, challenges, and why they could be the key to a more sustainable food future.

The Problem: Why Traditional Meat Production is Unsustainable
Traditional meat production is one of the most resource-intensive industries on the planet. Here’s why it’s a problem:
- Environmental Impact:
- Ethical Concerns:
- The industrial farming system often prioritizes efficiency over animal welfare. Animals are frequently raised in cramped, unsanitary conditions, leading to stress, disease, and the overuse of antibiotics. This not only raises moral questions but also contributes to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance.
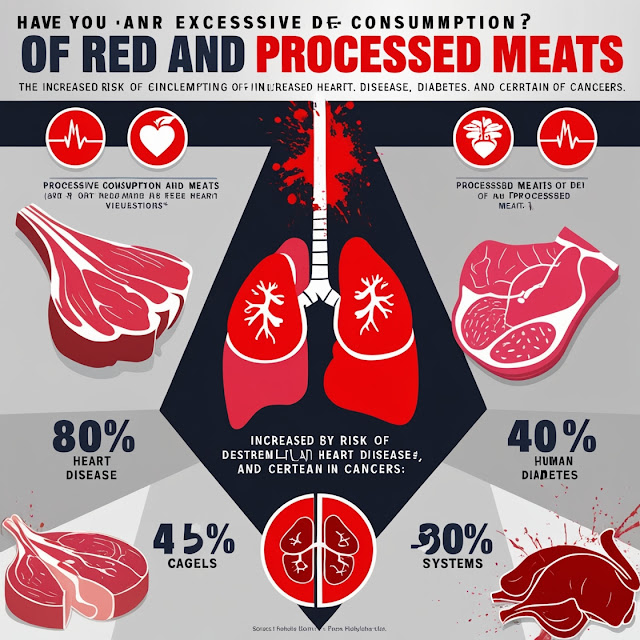
- Health Risks:
With the global population expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, the strain on our planet and resources will only intensify. It’s clear that we need a better way to produce meat—one that’s sustainable, ethical, and healthy.
The Agitation: Why Plant-Based and Cultivated Meat Alone Aren’t Enough
In recent years, plant-based meat alternatives have gained popularity. Brands like Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods have made significant strides in replicating the taste and texture of meat using ingredients like pea protein, soy, and beet juice. However, these products aren’t without limitations:
- Taste and Texture: While plant-based meats have come a long way, they still struggle to fully replicate the sensory experience of real meat. For many consumers, the difference is noticeable, which can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
- Nutritional Gaps: Some plant-based meats are highly processed and may lack essential nutrients found in animal proteins, such as vitamin B12, iron, and complete amino acid profiles.
On the other hand, cultivated meat—grown from animal cells in a lab—offers a closer match to traditional meat in terms of taste and nutrition. However, it comes with its own set of challenges:
3. High Production Costs: Lab-grown meat is currently expensive to produce, making it inaccessible to many consumers.
4. Environmental Concerns: A study from the University of California, Davis, found that the global warming potential of lab-grown meat, depending on the production methods used, could be four to 25 times greater than that of retail beef. This is largely due to the energy-intensive processes required to cultivate animal cells.
These limitations highlight the need for a middle ground—a solution that combines the best of both worlds.
The Solution: Hybrid Proteins to the Rescue
Hybrid proteins represent a balanced approach to addressing the shortcomings of both plant-based and cultivated meat. By blending plant-based ingredients with lab-grown meat, these products offer a sustainable, nutritious, and ethical alternative to traditional meat. Here’s how they work:
- Sustainable Production:
- Nutritional Benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Consumer Appeal:
- Hybrid proteins aim to deliver the taste and texture of real meat, addressing one of the biggest hurdles for plant-based alternatives. By meeting consumer expectations for flavor and mouthfeel, hybrid products have the potential to win over even the most dedicated meat lovers.
Case Study: Meatly’s Hybrid Protein Success
One company leading the charge in hybrid proteins is Meatly, a UK-based startup specializing in cultivated meat. Meatly has developed hybrid products that combine plant-based ingredients with lab-grown meat, creating a sustainable and nutritious alternative to traditional meat.
- Optimized Nutrition: Meatly’s hybrid products are designed to offer a balanced nutritional profile, with reduced saturated fat and increased fiber compared to conventional meat.
Environmental Impact: By blending plant-based ingredients with cultivated meat, Meatly has significantly reduced the carbon footprint of its products.
Cost Efficiency: The integration of plant-based components has allowed Meatly to lower production costs, making its products more affordable for consumers.
Meatly’s success demonstrates the potential of hybrid proteins to address the challenges of traditional meat production while meeting consumer demand for tasty, nutritious, and sustainable food options.
Nutritional Benefits of Hybrid Proteins
Hybrid proteins aren’t just good for the planet—they’re good for you, too. Here’s how they stack up nutritionally:
- Lower Saturated Fat: By incorporating plant-based ingredients, hybrid proteins can reduce saturated fat levels, which are linked to heart disease and other health issues.
- Higher Fiber Content: Plants are naturally rich in dietary fiber, which
supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Complete Protein: Cultivated meat ensures that hybrid proteins
contain all essential amino acids, making them a complete protein source.
- Micronutrients: Hybrid products can be fortified with vitamins
and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and vitamin B12, to meet nutritional
needs.
This combination of health benefits makes hybrid proteins an
attractive option for consumers looking to improve their diets without
sacrificing taste or convenience.
Consumer Acceptance and Market Potential
For hybrid proteins to succeed, they need to win over consumers. Fortunately, the growing awareness of sustainability and health issues is driving demand for ethical and nutritious food options. Here’s why hybrid proteins are well-positioned to capture this market:
- Health-Conscious Consumers: With more people prioritizing their health, hybrid proteins offer a way to enjoy meat without the associated health risks.
- Eco-Conscious Consumers: As concerns about climate change grow, consumers are seeking out sustainable alternatives to traditional meat.
- Flexitarians: The rise of flexitarianism—a diet that prioritizes plant-based foods while allowing for occasional meat consumption—creates a perfect audience for hybrid proteins.
By emphasizing the health and environmental benefits of hybrid proteins, brands can appeal to a wide range of consumers and drive adoption.
Challenges and Future Directions
While hybrid proteins hold immense promise, they’re not without challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles:
- Scaling Production:
- Consumer Education:
Despite these challenges, the future of hybrid proteins looks bright. With continued innovation and collaboration, they have the potential to revolutionize the global food system and create a more sustainable, ethical, and nutritious future.
Conclusion: The Future of Food is Hybrid
Hybrid proteins represent a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable and nutritious meat alternatives. By combining the best of plant-based and cultivated meat technologies, they offer a practical solution to the environmental, ethical, and health challenges of traditional meat production.
As the food industry continues to innovate, hybrid proteins are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable and health-conscious future. Whether you’re a meat lover, a flexitarian, or an eco-conscious consumer, hybrid proteins offer a way to enjoy the foods you love without compromising your values or the planet.
The future of food is here—and it’s hybrid.










Post a Comment